General Safe Driving Practices (Ghana Highway Code)
Keep your car in good condition by:
Regularly checking lights, brakes, steering, tires, direction indicators etc and clean windscreen and windows before moving.
Wear seatbelts
When on a motorcycle, scooter or moped, always wear a safety helmet.
Know all road signs.
Defensive driving tactics
Always:
Use your mirrors.
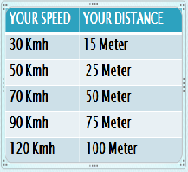
Keep to the speed limit, especially to 50 kmh (km per hour) in town.
Keep your distance to the car before you.
Mind pedestrians, cyclists and animals along the road.
Give way to ambulance, fire engines or police when their blue lights flash or two-tone horns sound.
Respect limits in the use of alcohol or medicine.
Emergency Situations:
How to Control your car
If a tire blows, do NOT slam brakes; control your steering wheel, steer right ahead and slowly stop.
Skidding Car

Skidding Car Sign

If a rear wheel skid happens, do NOT slam brakes: turn your steering wheel in the direction of the skid, as the car straightens out, straighten the front wheels.
In case of misbehavior of other road users: warn with horn and with flashlights, pull to the right as far as possible to allow them to pass.
If the accelaration pedal jams, turn off ignition and brake to a stop, leaving your car in gear!
If you have a breakdown:
Accidents:
Lines and Lane Control

Lines
Keep right when you plan no special action
Single broken line:

Check if the road is clear then overtake.
Double solid line:

You may NOT overtake under any circumstances.
Mixed line (Broken line and Solid line):

You may overtake, when the dotted line is on your side and the road is clear for overtaking.
Motorways

A motorway is a major road/dual carriageway that has been specially built for fast travel over long distances.
Due to the speed at which vehicles travel on motorways, the Highway Code advises against the use of the motorway by: Pedal cyclist, Animals, Pedestrians and hawkers, Motorcycles below the capacity specified in the Highway Code.
Vehicles are not allowed to Stop, Wait, Load or Offload, Park, Reverse, make U-turns etc on the motorway.
Difference between Highway and Motorway
A highway is a main, direct public road, especially a multi-lane, high speed thoroughfare connecting major population centers, whereas Motorway means a broad highway designed for high speed traffic, having restrictions on the vehicle types permitted and merging lanes instead of cross traffic.
Lanes
Dual carriageway (motorway only):
Keep right, when you have moderate speed go to the left for overtaking only.
Three-lane carriageway (motorway only):
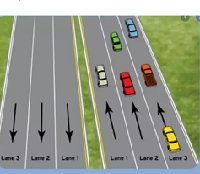
Keep right, when you have moderate speed stay in the middle, when slower vehicles are on your right go to the left for overtaking only. Avoid overtaking on the right side.
Lane 1 is the fast lane. Slow moving cars should avoid travelling in this lane
Lane 2 is the middle lane and it is for cars moving with moderate speed.
Lane 3 is the slow lane. Cars travelling at slower should always use this lane, especially trucks. Avoid overtaking in such lanes as much as possible.
Choose your lane early when turning left or right on the motorway:
Follow road markings and arrows in time! Do not enter areas marked with yellow stripes
Help Other Drivers to Join a Motorway
Other drivers would like to join the motorway as you also drive on it. When you notice that a driver wants to join the motorway, assist him/ her by:
• Slowing down and providing space for them.
• Speeding up if necessary and appropriate.
• Avoid trooping to race them while they are on the slip road/accceleration lane.
• Look ahead to find out whether there are vehicles about to join the motorway
• Be ready and prepared to adjust your speed.
• Move to the left-hand lane to make it easier and safer for joining traffic to merge
Overtaking
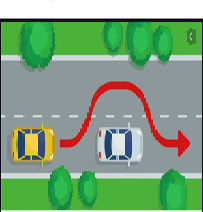
Check if the road is clear using your mirrors, signal before acting and overtake quickly and move back to the right.
Do NOT accelerate while being overtaken
Give way to cars coming towards you from the opposite direction.
On motorways avoid overtaking on the right side or snaking through the cars ahead of you.
Overtake on the left and return to the slow lane.
Do NOT overtake:

When coming to a junction, a crossing, a corner or bend, a bridge or a hill
When the road narrows
When you might hinder another car
When you would have to violate rules for lines and lanes
When there is a "no overtaking" road sign
Road Junctions

Look left, look right, look left again before crossing or turning; use your mirrors to double-check
On a level crossing, give way to a car from the left
On a priority junction:
When you have NO priority, stop at the "stop" or "give way" road sign; wait for a safe gap in the traffic before moving on
When you have priority, make sure other road users give way to you before moving on
When a mandatory road sign is present, follow indicated direction
When controlled by traffic lights, follow the lights, but make sure other road users give way before moving on at a green light
When controlled by a police officer, follow his/her directions at all times.
Roundabouts
A roundabout is an ordinary crossroad with one or more lanes, which encircles a central island. They may have one or more lanes.
It is required of all approaching vehicles to give way to vehicles already in the roundabout, therefore the risk of a vehicle colliding with another is reduced.

Turning right: stay to the right side of the road or choose the outer lane if two lanes are present (Orange arrow)
Going forward: you are free to choose the inside (green arrow) or the outside (blue arrow) of the roundabout, but once on the inside you should not turn right anymore (green arrows); likewise, when on the outside you should not go left (blue arrows)
Going left: use the inside of the roundabout or choose the inner lane if two lanes are present (green arrows)
When approaching a roundabout give way to a car from the left
When on the roundabout follow directions for turning right, going straight forward and going left:
Roundabout ahead

This road sign tells you that you are about 50m away from the roundabout.
Compulsory Roundabout

This road sign informs you that you are closer to the roundabout.

A broken line across the carriageway means you should give way to traffic in the roundabout.
Reversing
Make sure no one is behind you, particularly pedestrians and children
When you cannot see clearly: get a guide
Never reverse from a side road into a main road
Lights
Use headlamps where there is no street lighting
Use dipped headlamps in build-up areas
Dip your lamps when meeting other cars
If you are dazzled by other cars, slow down
Use headlamps when there is mist
Waiting and Parking

No Parking

No waiting
Do NOT park where:
There is a prohibitory road sign
It would be difficult for others to see clearly
It would be a danger to others
It would hold up traffic or make the road narrow
Emergency vehicles stop
Take care when opening a door when leaving, use your handbrake, turn off lights and always lock your car.
Double Parking
The Road Traffic Regulation forbids parallel parking which is referred to as double parking. Each time you are about to park a vehicle, ask yourself the following questions:
Is it safe?
Is it convenient to other road users?
Is it legal
Breakdowns and Accidents

If you have a breakdown:
Get your car off the road
Flash the amber direction indicators
Place the red reflecting triangle 50 meters behind your car and another in front.
Accidents:
If there is no help: give first aid
If there is help available: pass slowly and follow directions of police
Railway level crossings
Keep your distance at any level crossing
Do not cross a railway once the red lights have started to flash
At crossings without gates: always stop, look both ways, listen carefully if there is no train coming
If you start crossing and the red lights start flashing: keep going, do not stop.
Railway level crossings
Pedestrian Responsibilities
Pedestrians (including joggers) should be aware of traffic conditions. Watch out for drivers before assuming you have the right-of-way when crossing a street. Yield the right-of-way to vehicles when you cross a street between intersections and in areas with no pedestrian crosswalks or signals.

Precautions
If there are no sidewalks, walk facing oncoming traffic:
Do not walk or jog on any freeway where signs tell you that pedestrians are not allowed.
Do not walk or jog in a bike lane unless there is no sidewalk.
Pedestrians should face on-coming traffic if walking by the roadside.
Precaution to take at Night
Make yourself more visible by:
Wearing white, light, or reflective material.
Carrying a flashlight.
Vehicles with New Technology
Your vehicle may have technology that allows you to have cell phone conversations or play music from an electronic device. With the increase of such technologies, it is important to remain aware of the road and avoid driving distractions.
Tips To Reduce Technological Distractions:
Do not input navigation instructions while driving.
Do not adjust music or other electronic devices while driving.
For navigation devices, use the audio navigation function when possible.
OCCUPANT PROTECTION
Seat Belts
Seat belts, both the lap belt and shoulder harness, will increase your chance of survival in most types of collisions.
The seat belts must be in good working order and used by all passengers.
If a passenger is not old enough to use a seat belt then he/she must be seated in an approved child passenger restraint system.
Always use your seat belts (including the shoulder harness) even if the vehicle is equipped with air bags.
You can have shoulder harnesses or seat belts installed in older vehicles.
If you wear a lap and shoulder belt, your chances are 3 to 4 times higher to live through a collision. If your vehicle is equipped with a separate lap and shoulder belt, you are required to use both the lap and shoulder belts.
What is the Right Car Seat?

The right car seat is one that fits your child and your vehicle, and is one you will use correctly every time you travel.
The general child restraint basics and the common steps are:
Infants should use rear-facing infant seats. Toddlers should use forward-facing child safety seats. Older children should use booster seats until they properly fit a seat belt.
Rear-Facing Infant Seats

Always use rear-facing infant seats for infants. These types of seats are designed to be portable and are generally lighter in weight and easier to carry.
They should be used according the car seat manufacturer’s directions and until the child reaches the top height or weight limit allowed for the seat. Laws often require children less than 1 year and under 20 pounds to be in a rear-facing child seat.
Forward-facing Car Seats

Once a child outgrows the rear-facing car seat, it is ready to travel in a forward-facing car seat with a harness. Children in this group are typically four to seven years old.
Booster Seats

When outgrowing the forward-facing car seat with a harness, it is time to travel in a booster seat.
Booster seats are recommended for children until they are big enough to properly use a seat belt.
Children Should Ride in the Back Seat
The law requires all children to ride in the back seat whenever possible.
Generally, you should keep a child in the back seat at least through age 12.
Pregnant women should wear the lap belt as low as possible under the abdomen, and the shoulder strap should be placed between the breasts and to the side of the abdomen’s bulge.
WARNING: Using seat belts reduces the risk of being thrown from your vehicle in a collision.
If you do not install and use a shoulder harness with the seat (lap) belt, serious or fatal injuries may happen in some collisions.
Lap-only belts increase the chance of spinal column and abdominal injuries especially in children.
Child Restraint System and Safety Seats
Your child must be secured by either an approved child passenger restraint system or a safety belt depending on his/her height and age.
Children under 8 years old must be properly secured in an approved child passenger restraint system.
Children under 8 years old may ride in the front seat of a vehicle in an approved child passenger restraint system under the following instances:
There is no rear seat.
The rear seats are side-facing jump seats.
The rear seats are rear-facing seats.
The child passenger restraint system cannot be installed properly in the rear seat.
All rear seats are already occupied by children 7 years old or younger.
Medical reasons require the child to not ride in the back seat.
A child may not ride in the front seat of an airbag equipped vehicle if he/she:
Is in a rear-facing child passenger restraint system.
Is less than 1-year-old.
Riding Safely with Air Bags
Air bags are safety features that help keep you safe alongside the seat belt.
The biggest risk is being too close to the air bag.
An air bag needs about 10 inches of space to inflate. Ride at least 10 inches (measured from the center of the steering wheel to your breastbone) from the air bag cover, if you can do this while maintaining full control of the vehicle.